PREIMPLANTATION GENETIC DIAGNOSIS FOR BRCA 1/2 CARRIERS
A
Assisted Embryo Hatching
a procedure in which a hole is made in the zona pellucida of the early embryo. The embryo may more easily “hatch” out of the zona through the hole prior to implantation.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
a collective term which refers to a variety of medical procedures used to achieve pregnancy.
B
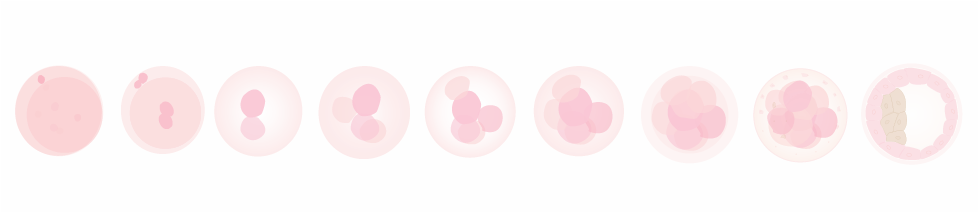
Blastocyst
the stage of development that the embryo is in when it enters the uterine cavity for implantation (typically 5-6 days after fertilization). It is comprised of two types of cells; an outer layer of cells called the trophoblast that will become the supporting tissue of the embryo such as the placenta and an inner layer referred to as the Inner Cell Mass, which will be multiply and contribute to the cells of the embryo.
Blastomere
a single cell from the developing 3-day embryo.
C
Cryopreservation
halting the embryo development before implantation through a freezing procedure.
Controlled Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH)
the use of medications to stimulate growth and development of multiple ovarian follicles.
F
Follicle
a structure in the ovary that has nurtured the ripening egg and from which the egg is released or retrieved.
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
a hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates the ovary to ripen a follicle for ovulation.
Fluorescent in-situ hybridization (FISH)
a type of visualization used to determine the chromosome number and chromosomal mutation status of the embryo via PGD or PND.
G
Genetic counselor
a medical professional with specialized training in clinical genetics.
I
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
an assisted fertilization technique in which a sperm is micro injected directly into the egg cytoplasm.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
a procedure during which an egg is removed from a ripe follicle and fertilized by a sperm outside the human body.
L
Linkage Analysis
involves the study of BRCA1/2 inheritance patterns within a family and the identification of genetic markers that map near the gene. These genetic markers are physically linked to the gene.
M
Meiosis
this term describes cell division that occurs during the formation of the mature egg and sperm. During meiosis, the number of chromosomes (genes) is reduced so that the egg and sperm contribute only half of the parent’s genes to the embryo.
O
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Stimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
a medical complication of the stimulation procedures and medications in which stimulated follicles produce excess hormones and other factors which may lead to serious complications and may cause cancellation of a cycle and for a small number of women may result in death.
P
Polar body
a polar body is a small cell that is naturally released by the egg or oocyte during the process of meiosis. The first polar body is released by the oocyte near the time of ovulation. The second polar body is released by the oocyte, at the time of fertilization. The polar bodies do not contribute to the developing embryo, but are naturally discarded by the oocyte during the process of meiosis. Because the polar body contains one half of the possible genetic information of the mother, the genetic information of the oocyte can be inferred by the genetic testing of the polar body.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
one of the most widely used laboratory techniques for visualizing genetic information and can be used for PGD or PND.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
refers to procedures that are performed on embryos prior to implantation, sometimes even on oocytes prior to fertilization to determine gene status.
Prenatal Diagnosis (PND)
testing for genetic mutations in a fetus during the first or second trimester of pregnancy.
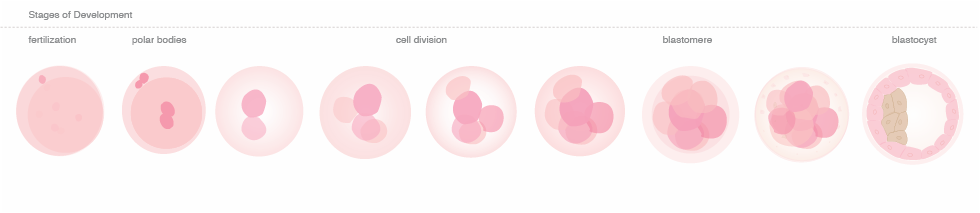
A Visual Guide to BRCA and PGD:
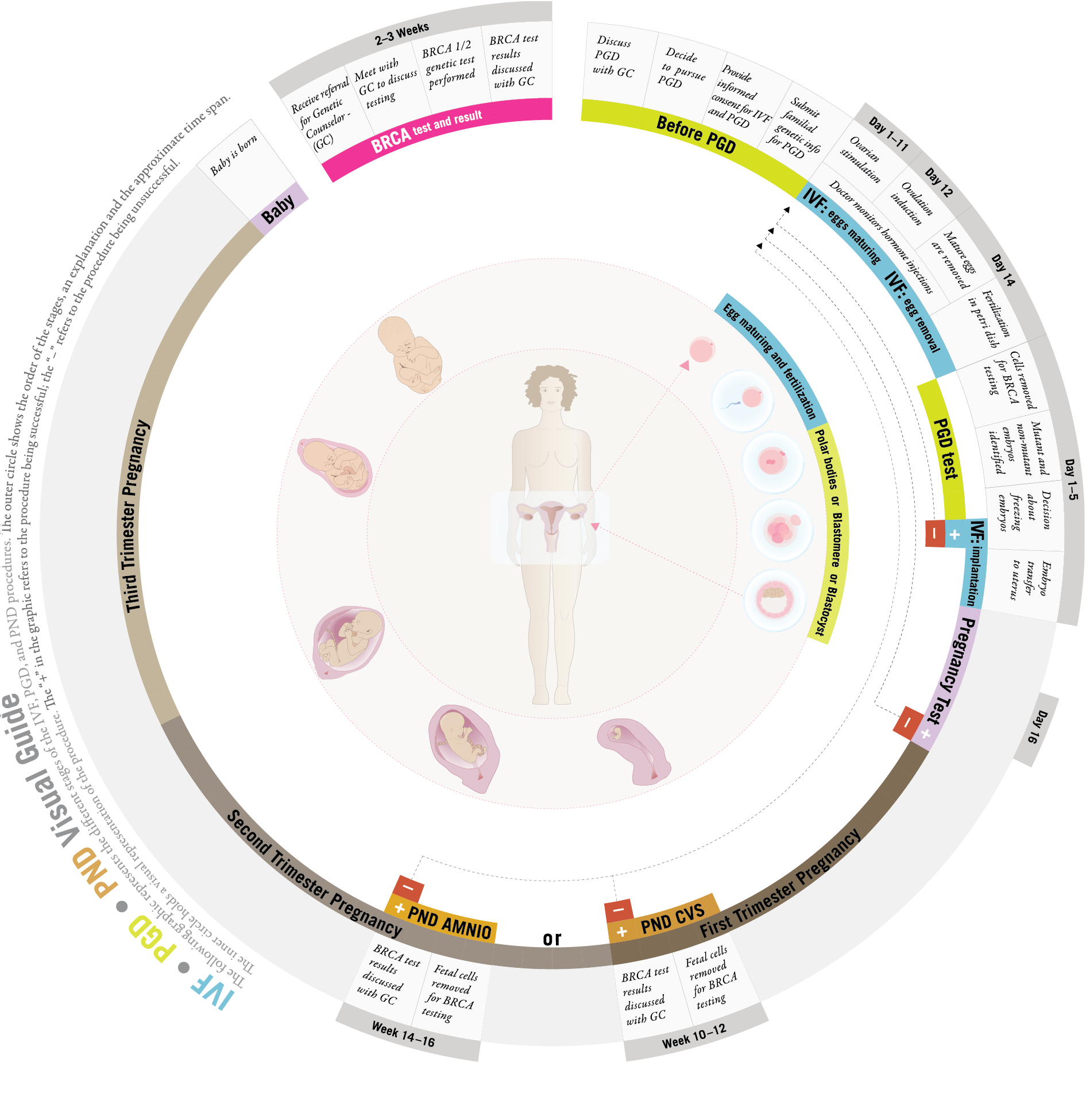
The following graphic represents the different stages of the IVF, PGD, and PND procedures. The outer circle shows the order of the stages, an explanation and the approximate time span. The inner circle holds a visual representation of the procedure.
The "+" in the graphic refers to the procedure being successful; the "–" refers to the procedure being unsuccessful.
When is PGD Done:
Introducing PGD
PGD is a multi-stage process that screens embryos for presence of mutations before pregnancy is established, such that couples may choose to implant embryos free of the BRCA mutation. PGD allows for the genetic testing of an embryo for various genetic mutations. To date, over 3000 children have been born as a consequence of PGD testing for a variety of conditions. In the case of BRCA, PGD allows parents to have a child that is at a greatly reduced risk of being born a mutation carrier. PGD involves the laboratory screening of embryos for the presence of mutation before it has been implanted inside the uterus. Since PGD is a laboratory test that screens multiple embryos, the use of an accompanying technology, in vitro fertilization (IVF), is required.
PGD incorporates multiple technologies
- Assisted Reproductive Therapy (In Vitro Fertilization)
- Investigative Genetic Testing of Embryos (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis)
- Confirmation Genetic Testing of Fetal/Placental Tissues: Pre Natal Diagnosis (Chorionic Villi Sampling/Amniocentesis)
Ovarian Stimulation
Since it is necessary to test more than one embryo, IVF is used to help you produce many eggs at once. Shortly after you begin your menstrual cycle, fertility hormones will be administered to stimulate the production of multiple oocytes (eggs). These hormones are administered through injection, and it is necessary to have a doctor monitor your hormone levels during this time, as well as conduct an ultrasound to monitor oocyte development.
Fertilization
After the mature eggs are removed, they will be taken to a lab and prepared for fertilization. Fertilization is most commonly performed by injecting a single sperm into an egg in a process called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI).
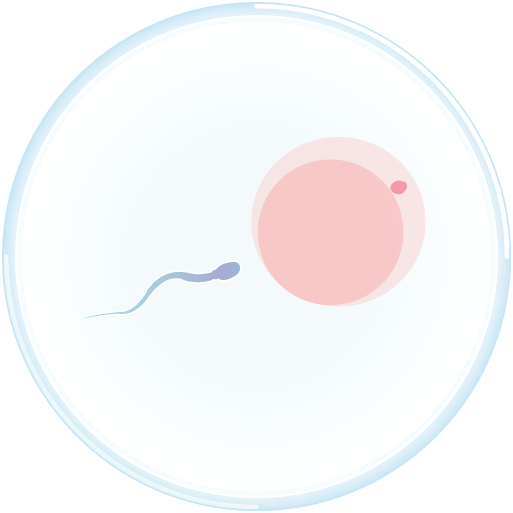
Image 1: Fertilization in a Petri dish